The road to (preventing) diabetes
 Diabetes is a long-lasting (chronic) health condition that affects how your body converts sugar to energy. When we eat, the food is broken down into glucose (type of sugar) and released into the bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, your pancreas releases insulin that allows the cells in your muscles, fat, and liver to absorb glucose from your blood. People with diabetes cannot either make enough insulin or cannot use the insulin they make. It means that too much glucose stays in the bloodstream, which over time can damage the blood vessels and cause heart and kidney diseases and even vision loss. Lab testing, diet, and routine exercise are the road to preventing diabetes.
Diabetes is a long-lasting (chronic) health condition that affects how your body converts sugar to energy. When we eat, the food is broken down into glucose (type of sugar) and released into the bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, your pancreas releases insulin that allows the cells in your muscles, fat, and liver to absorb glucose from your blood. People with diabetes cannot either make enough insulin or cannot use the insulin they make. It means that too much glucose stays in the bloodstream, which over time can damage the blood vessels and cause heart and kidney diseases and even vision loss. Lab testing, diet, and routine exercise are the road to preventing diabetes.
So, what is the road to preventing diabetes?
There are two types of diabetes, type 1 and type 2. In type 1, the immune system attacks the pancreas by mistake, which leads to it producing little or no insulin. Different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to type 1 diabetes. Although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults. Treatment focuses on managing blood sugar levels with insulin shots, diet, and lifestyle. In type 2, the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or resists insulin. The main risk factors for type 2 diabetes are being overweight, not physically active (less than 3 times a week), family history, or being prediabetic. Prediabetes is when your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. It is possible to delay and even prevent diabetes type 2 by changing your lifestyle -- losing weight (if you are overweight), eating healthy food, and being physically active. If you ask yourself, “How do I know if I’m prediabetic?” The answer is simple: check your hemoglobin a1c (A1c, or HbA1c). Multiple providers offer online at home A1c lab test.
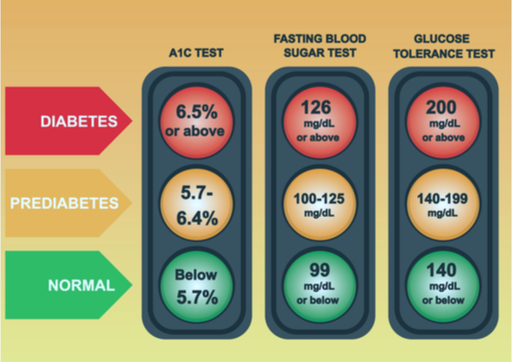
The A1C test measures your average blood sugar level over the past 2 or 3 months. An A1C below 5.7% is normal, between 5.7 and 6.4% indicates you have prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher indicates you have diabetes. These levels are for both diabetes type 1 and type 2. The other diabetes tests are the Fasting Blood Sugar Test – you would need to fast for 8 to 10 hours before the test, and the Random Blood Sugar Test - you can take this test at any time and don’t need to fast. In both tests, the glucose level in your bloodstream is measured. The random test helps to manage diabetes and check if the glucose level in your bloodstream is not too high. It can also help diagnose new diabetes cases if the glucose level is very high (glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher), but this test cannot identify prediabetes. Only the Fasting Glucose test can differentiate between normal, prediabetes, and diabetes cases.
If your test results show you have prediabetes, take it seriously and try to change your lifestyle. Ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle program in your area and keep measuring your hba1c levels every 2-3 months.
The third type of diabetes test is the Glucose Tolerance Test. This test measures your blood sugar before and after you drink a liquid that contains glucose. You’d need to fast overnight before the test and have your blood drawn to determine your fasting blood sugar level. Then you’ll drink the liquid and your blood sugar level will be checked 1 hour, 2 hours, and 3 hours after ingestion. At 2 hours, a blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL or lower is considered normal, 140 to 199 mg/dL indicates you have prediabetes, and 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes. This test is done in clinics and does not available online. Gestational diabetes is diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy by the glucose tolerance test. Expectant mothers can help control gestational diabetes by eating healthy foods, exercising, and sometimes taking medication when necessary.